Multiple Correspondence Analysis (MCA) is an extension of simple CA to analyse a data table containing more than two categorical variables. Fvizmca provides ggplot2-based elegant visualization of MCA outputs from the R functions: MCA in FactoMineR, acm in ade4, and expOutput/epMCA in ExPosition. Read more: Multiple Correspondence Analysis Essentials. Fvizmcaind: Graph of. Biplot (coefs,Name,Value) specifies additional options using one or more name-value pair arguments. For example, you can specify 'Positive','true' to restrict the biplot to the positive quadrant (in 2-D) or octant (in 3-D).
- 2 BiplotGUI: Interactive Biplots in R 1.1. Biplots Introduced byGabriel(1971), the biplot is described byGower and Hand(1996) in their authoritative monograph as the multivariate analogue of the ordinary scatter plot. As such, biplots are representations of multivariate data in which information on both the samples.
- Scoreallseveneventsinthesamedirection heptathlonc(14,25),## hurdles highjump shot run200m longjump javelin run800m ## Braun (FRG) 13.71 1.83 13.16 24.78 6.12 44.58.
- Only the default is a biplot in the strict sense. The variables are scaled by lambda ^ scale and the observations are scaled by lambda ^ (1-scale) where lambda are the singular values as computed by princomp. Normally 0 biplot.
Biplot of Multivariate Data
Plot a biplot on the current graphics device.
- Keywords
- multivariate, hplot
Usage
Arguments
The biplot, a fitted object. For biplot.default, the first set of points (a two-column matrix), usually associated with observations.
The second set of points (a two-column matrix), usually associated with variables.
Casino moons casino instant players club. If TRUE the second set of points have arrows representing them as (unscaled) axes.
A vector of length 2 giving the colours for the first and second set of points respectively (and the corresponding axes). If a single colour is specified it will be used for both sets. If missing the default colour is looked for in the palette: if there it and the next colour as used, otherwise the first two colours of the palette are used.
The character expansion factor used for labelling the points. The labels can be of different sizes for the two sets by supplying a vector of length two.
A vector of character strings to label the first set of points: the default is to use the row dimname of x, or 1:n if the dimname is NULL.
A vector of character strings to label the second set of points: the default is to use the row dimname of y, or 1:n if the dimname is NULL.
An expansion factor to apply when plotting the second set of points relative to the first. This can be used to tweak the scaling of the two sets to a physically comparable scale.
The length of the arrow heads on the axes plotted in var.axes is true. The arrow head can be suppressed by arrow.len = 0.
Limits for the x and y axes in the units of the first set of variables.
graphical parameters.
Details
A biplot is plot which aims to represent both the observations and variables of a matrix of multivariate data on the same plot. There are many variations on biplots (see the references) and perhaps the most widely used one is implemented by biplot.princomp. The function biplot.default merely provides the underlying code to plot two sets of variables on the same figure.
Graphical parameters can also be given to biplot: the size of xlabs and ylabs is controlled by cex.
Side Effects
a plot is produced on the current graphics device.
References
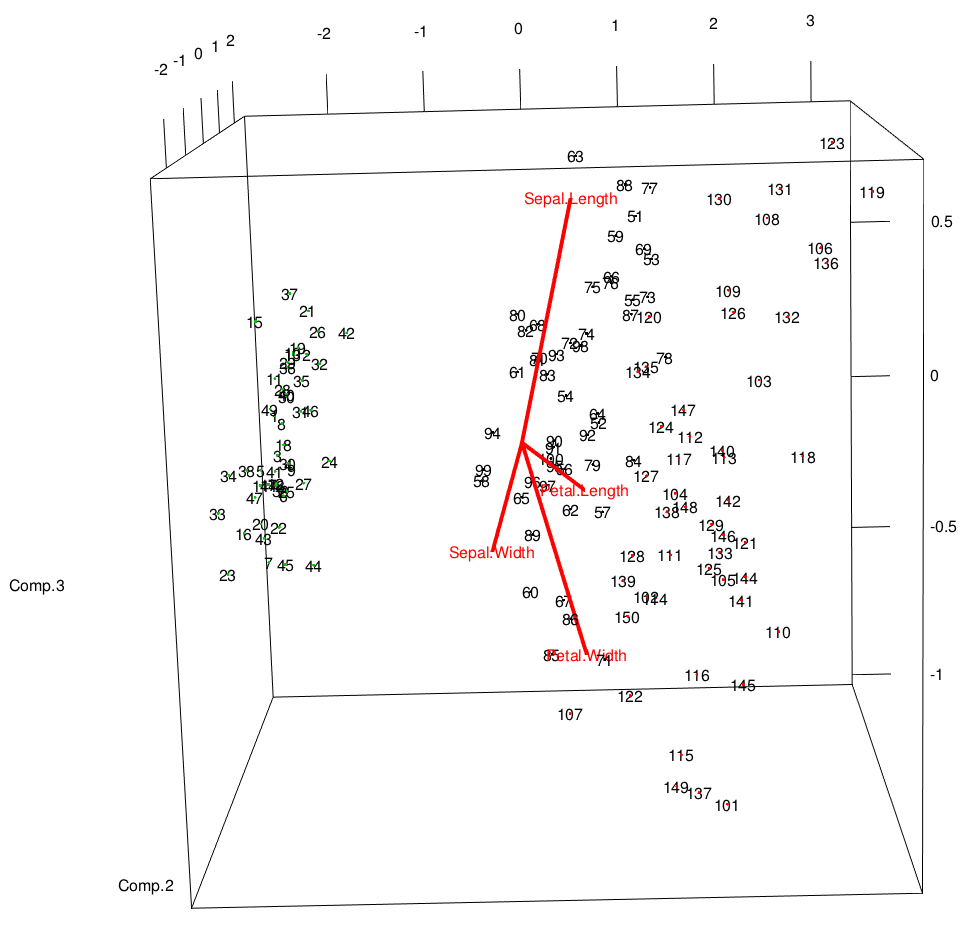
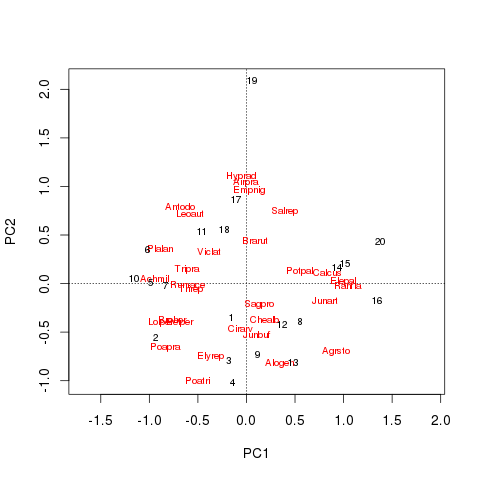
R Biplot Examples
K. R. Gabriel (1971). The biplot graphical display of matrices with application to principal component analysis. Biometrika, 58, 453--467. 10.2307/2334381.
- Keywords
- multivariate, hplot
Usage
Arguments
The biplot, a fitted object. For biplot.default, the first set of points (a two-column matrix), usually associated with observations.
The second set of points (a two-column matrix), usually associated with variables.
Casino moons casino instant players club. If TRUE the second set of points have arrows representing them as (unscaled) axes.
A vector of length 2 giving the colours for the first and second set of points respectively (and the corresponding axes). If a single colour is specified it will be used for both sets. If missing the default colour is looked for in the palette: if there it and the next colour as used, otherwise the first two colours of the palette are used.
The character expansion factor used for labelling the points. The labels can be of different sizes for the two sets by supplying a vector of length two.
A vector of character strings to label the first set of points: the default is to use the row dimname of x, or 1:n if the dimname is NULL.
A vector of character strings to label the second set of points: the default is to use the row dimname of y, or 1:n if the dimname is NULL.
An expansion factor to apply when plotting the second set of points relative to the first. This can be used to tweak the scaling of the two sets to a physically comparable scale.
The length of the arrow heads on the axes plotted in var.axes is true. The arrow head can be suppressed by arrow.len = 0.
Limits for the x and y axes in the units of the first set of variables.
graphical parameters.
Details
A biplot is plot which aims to represent both the observations and variables of a matrix of multivariate data on the same plot. There are many variations on biplots (see the references) and perhaps the most widely used one is implemented by biplot.princomp. The function biplot.default merely provides the underlying code to plot two sets of variables on the same figure.
Graphical parameters can also be given to biplot: the size of xlabs and ylabs is controlled by cex.
Side Effects
a plot is produced on the current graphics device.
References
R Biplot Examples
K. R. Gabriel (1971). The biplot graphical display of matrices with application to principal component analysis. Biometrika, 58, 453--467. 10.2307/2334381.
J.C. Gower and D. J. Hand (1996). Biplots. Chapman & Hall.
See Also
biplot.princomp, also for examples.
Aliases
- biplot
- biplot.default

